We are in a period of tremendous telecommunications change and technology-led disruption. At American Tower, we are focused on the intersection between our real estate assets, emerging technologies, and the wide-ranging wireless use cases that will change the ways we live, work, and play in an increasingly digital world. We’re not yet experiencing true 5G, but we know its full, nationwide implementation will support everything from a future consumer-driven metaverse to enterprise solutions, such as autonomous delivery systems, sophisticated manufacturing, and warehouse automation.
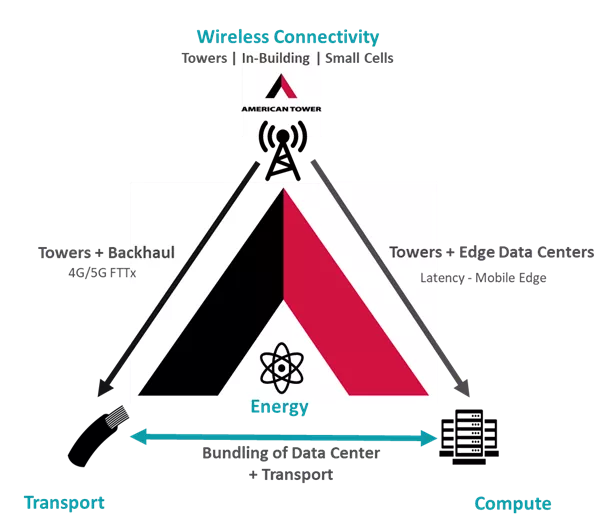
As more aspects of our lives become digitalized, there will be huge amounts of data. While today’s predominant business model involves cloud computing and centralized data processing, use cases will increasingly need to source and retrieve data at the edge, as close as possible to where the best application processing and lower cost of networking will occur. This helps ensure low latency, that is, a network that can process a high volume of data with minimal end-to-end, round-trip delay. Our distributed towers, handling the growing demands for wireless data, can aid in meeting these future needs. While the underlying real estate assets are passive, we can add value by offering collocation space, power, networking, and compute capabilities. Some examples of these possibilities follow below.
Extending the Core
While the core of our business model is based on property rights and rights of way, the needs of an increasingly digitalized world offer important opportunities to extend our core, often through new partnerships in power and energy as a service, computing, transport, and wireless connectivity.
To drive enhanced wireless connectivity, for example, we are focused on advances in neutral-host networks for in-building systems, shared “Radio Access Network (RAN) as a Service” opportunities in rural networks, and multitenant satellite systems to extend coverage.
5G signals can have difficulty penetrating buildings, both homes and offices. A shared network, working off neutral-host infrastructure, like CBRS or carrier Wi-Fi networks, allows for better buildout of a location and supports an open platform for innovation and development of new use cases. With today’s highly fragmented in-building services, a multi-operator shared network also makes it easier for enterprises to leverage private 5G and for operators to connect their customers using their existing services. American Tower is piloting this in Germany, Mexico, and the United States.
Rural areas will benefit from partnerships between satellite communications firms and independent telecom tower companies (TowerCos), with satellite and terrestrial networks working together to close coverage gaps and foster contiguous connectivity. American Tower macro site infrastructure can provide space, power, and networking for the gateways connecting the terrestrial internet and RAN to the satellite. The satellite will rebroadcast signals over wide areas to bring mobile services to unserved and underserved areas. The user device then detects the presence of this expanded coverage and sends signals to the satellite to access the network and essentially fill the gaps or “white spaces” of the terrestrial network.
We’re also excited about edge compute. What’s the edge? If it’s your car processing data to assist in advanced driver assistance systems, emanating from sensors and cameras, your car is the edge. Now imagine the car takes a 5G broadband connection and sends data to the nearest tower, which—as an added benefit—means your car uses less battery to process certain tasks because it is computed at the tower. Sites equipped with edge data centers can handle greater amounts of 5G data, deliver compute power, and ensure a faster response time, which may translate to safer, more efficient roads and fewer emissions.
Smart mobility solutions contribute to safety in many ways, from alerting workers to danger in a work zone to improving the safety of an intersection for pedestrians via traffic lights and other information sent to smart phones. Neutral-host infrastructure utilized in Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything systems can enhance quality of life from the perspective of traffic flows, pedestrian needs, and the viability of different transport options. The right mobility solutions may also be important from an equity standpoint, allowing for better transport to certain areas of a city or region and thereby making jobs more accessible.
The rentable space at our towers creates various demands for ancillary services, such as energy storage, that draw on the power and improved fiber connectivity at our sites. We are already seeing demand for the use of tower assets to support more localized data centers. Utilizing distributed data centers—small, local computing facilities—we can improve future 5G use cases. In the traffic intersection example above, we could see vehicles react more quickly, if data does not need to travel to a centralized processing hub.
Moreover, consider the recent experience with unreliable electrical grids in Texas and California. Wind and solar are intermittent resources, necessitating energy storage to reliably support renewable grid capacity. Distributed shared battery plants at tower sites can improve resiliency, regulate the load, and move it to a better demand cost point. These capabilities will improve the ability to deploy power-intensive 5G with cleaner, renewable energy.
TowerCos Must Become Digital InfraCos
In short, TowerCos will need to transform into digital infrastructure companies (InfraCos). A more digital society will require massive, distributed infrastructure to support low-latency applications, leveraging 5G and the Internet of Things innovations. Multiuse developments and smart cities will also require a digital infrastructure investment, including public and private partnerships.
Such projects extending over a decade or more require a long-term, financially stable developer and promoter. Neutral-host infrastructure providers like American Tower are best suited to provide this.
We look forward to the role our towers can play in this global transformation, and to helping consumers and society benefit from the full promise of 5G.